Imagine a world where the great Library of Alexandria remained intact, safeguarding the rich history of translation through its scrolls and manuscripts. These ancient texts could have provided unparalleled insights into how translation has connected civilizations across time.
In that alternate reality, we might have unveiled a precise timeline of how ideas and cultures intermingled through the art of translation.
Instead, what remains are fragments of the history of translation that provoke debate among historians, leaving us to piece together the evolution of translation. However, it’s agreed that translation dates way back before the Bible.
In this article, we’ll journey through time, opening the doors to the past to the many theories of the evolution of translation.
The Beginnings: Ancient Translation Practices
The history of translation can be traced back to the Sumerian poem ‘Epic of Gilgamesh,’ one of the earliest known examples of cross-cultural translation. Around 2000 BC, this text was translated into multiple Asian languages, marking the beginning of a long and fascinating history of translation practices.
Its translations helped to bridge the cultural gap between the Mesopotamian and Asian civilizations, allowing for the exchange of stories, morals, and wisdom that shaped societies for centuries.
The Rosetta Stone: Key to Understanding History
Another pivotal moment in translation history occurred with the discovery of the Rosetta Stone. This artifact, inscribed with the same text in three different scripts—Greek, Demotic, and Egyptian hieroglyphics—was instrumental in deciphering the complex writing system of ancient Egypt.
Buddhist Translations: A Spiritual Exchange
The translation work of Buddhist monks in China was equally transformative. As these monks translated Indian texts into Chinese, they played a crucial role in the dissemination of spiritual and philosophical ideas, such as karma, dharma, and enlightenment.
| Get the same level of precision as the ancient Buddhist translations of ancient texts through our Chinese legal translation services. |
Sacred Text Translations: Quran and Bible History of Translation
Religious translation pioneers conducted the translation of religious texts, most notably the Quran and Bible, facilitating the spread of their ideologies across cultures and languages.
The Septuagint: A Foundation for Future Translations
The Septuagint laid the groundwork for modern translation techniques of biblical texts. Its use in early Christian communities helped disseminate the teachings of Christianity beyond the boundaries of Hebrew culture, influencing subsequent translations of the Bible into Latin and other languages.
The Vulgate: Jerome’s Masterpiece
Commissioned by Pope Damasus I, Jerome sought to create an accurate and accessible version of the Scriptures for the Latin-speaking populace.
The Vulgate became the Catholic Church’s official version of the Bible for over a millennium, influencing theological thought and contributing to the uniformity of Christian doctrine across Europe.
Quran Translation History
The Quran was revealed in classical Arabic, and many scholars argue that translating it into other languages can lead to a loss of the original meanings and nuances. Despite this, translations have been undertaken in various languages to spread the teachings of Islam globally.
From Medieval Translation Methods to Renaissance Translation History
From the medieval era to the Renaissance, the history of translation saw remarkable advancements. Scholars developed new methods and debated approaches, laying the foundation for modern translation techniques still used today. A development of translation that didn’t only enhance communication, but also set the stage for the modern practices we recognize today.
The Toledo School of Translators
Located in Spain and active during the 12th and 13th centuries, this school united scholars from diverse backgrounds, including Muslims, Christians, and Jews.
These translators dedicated themselves to translating Arabic, Latin, and Hebrew texts into various European languages. Their efforts primarily focused on translating essential works in philosophy, science, and medicine.
Renaissance Debates: Literal vs. Sense-for-Sense Translation
As intellectual pursuits flourished during the Renaissance, debates arose regarding the best methods of translation. At the heart of these discussions were two primary approaches: literal (word-for-word) translation and sense-for-sense translation.
Advocates of literal translation argued that it maintained the integrity of the original text, preserving its exact meanings and nuances.
Conversely, those in favor of sense-for-sense translation contended that it was essential to convey the intended meaning and context of the original work, even if that meant departing from a word-for-word rendering.
| Our technical translation services are designed to enhance multilingual communications. |
Influential Translation Theorists and Historical Approaches to Translation
Translation has a rich intellectual history shaped by various theorists and their differing perspectives on the translation process.
Cicero and Horace: Metaphrase vs. Paraphrase
Cicero, the renowned Roman statesman and philosopher, articulated fundamental theories of translation that distinguished between two approaches: metaphrase and paraphrase. Metaphrase refers to a literal translation, where the translator adheres closely to the original text’s words and structure.
In contrast, Horace, a contemporary of Cicero, advocated for paraphrase—also known as sense-for-sense translation. This approach emphasizes capturing the essence and meaning of the original text while allowing for more flexibility in expression.
John Dryden’s Balanced Approach
In the 17th century, John Dryden further contributed to translation theory by proposing a balanced approach that considered both the need for fidelity and the importance of naturalness in the target language.
Functionalism in Translation History
As translation theories progressed into the 20th century, a significant shift occurred with the emergence of functionalism.
Functionalists argue that translation decisions should hinge on the intended function of the text—whether it aims to inform, persuade, entertain, or fulfill another role—and adapt accordingly.
Translation and Globalization
The modern era has witnessed transformative shifts in translation driven by pivotal societal changes, particularly during the Industrial Revolution and the rise of globalization.
The Industrial Revolution: Increased Demand for Translation
The Industrial Revolution, beginning in the late 18th century, marked a significant turning point in manufacturing and economic expansion. As industries grew and international trade blossomed, so did the need for translation services.
Role of Translation in Globalization
The arrival of the Internet further accelerated the evolution of translation, breaking down geographical barriers and enabling instant communication across borders.
Companies realized that to succeed in foreign markets, they needed more than just translation; they required localization—adapting their products and services to meet the local culture’s needs and preferences.
Cultural Adaptation in Modern Translation Practices
In the modern history of translation, cultural adaptation—also known as transcreation—has become a cornerstone of effective communication. Translators now prioritize understanding the cultural nuances of their target audience, ensuring that the history of translation continues to evolve in meaningful ways.
This goes beyond mere word-for-word translation; it involves a deep understanding of the target audience’s cultural context, values, and emotional responses.
| Our accurate document translation services foster global collaborations. |
History of Machine Translation and the Rise of Translation Software
The journey of machine translation (MT) began in the mid-20th century, marking a revolutionary shift in the way we approach language translation.
Early History of Machine Translation
The groundwork for machine translation was laid during the 1940s and 1950s. The first significant attempts at machine translation stemmed from the need for immediate translation of Russian scientific and technical documents during the Cold War.
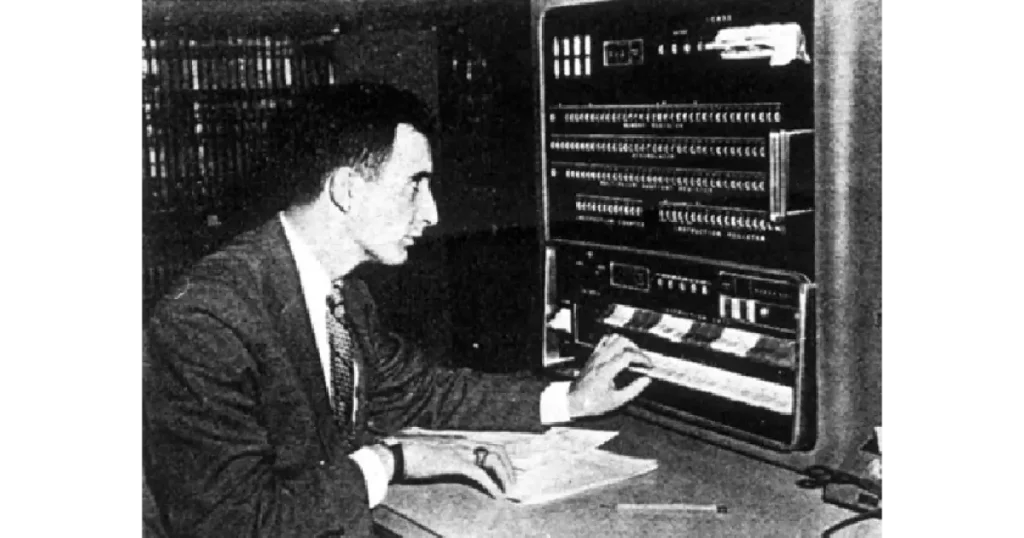
Notably, in 1954, the Georgetown-IBM experiment showcased the potential of translating simple Russian sentences into English using early computers.
However, these early translation tools were too simple, relying on word-for-word translations.
Evolution of Translation Software
From those early days, machine translation has significantly evolved, especially with the emergence of artificial intelligence (AI) and natural language processing (NLP).
The introduction of statistical machine translation in the 1990s marked a significant shift, leveraging vast amounts of bilingual text data to generate smarter translations. The strong impact of technology on translation allowed machines to learn patterns between languages, improving accuracy and fluency.
Today, advanced neural machine translation (NMT) models have taken center stage, using deep learning techniques to produce more natural-sounding translations.
Need help with your global expansion? For 12 years, AsiaLocalize has been helping thousands of clients enter the Asian markets with high-quality translation and localization services, specifically catering to their audiences.
| Thrive in Asian Markets! Contact Our Experts Now. |