Ensuring accuracy in translated materials is the most important aspect we all look forward to, especially when dealing with critical sectors like pharmaceutical content, legal documents, or medical devices.
So, is there a way or a service where we can make sure of translation accuracy?
Yes, back translation is an effective way and the strongest quality control method. This method ensures the original meaning is clear and free from errors or misunderstandings. Let’s learn more about it, why it is important, and when to use it.
What Is Back Translation?
Back translation refers to the process of translating content from the target language back into the source language. This method allows for a double-check of the original translation, helping to catch potential mistakes, cultural nuances, or context misinterpretations.
The goal is to maintain linguistic equivalence and accuracy, especially in documents where even minor mistakes can have significant consequences. By comparing the back-translated document to the original, it is easier to identify discrepancies that may have been overlooked in the first translation and ensure your message remains intact across languages.
When Should You Use Back Translation?
Back translation is particularly useful when translating documents that are critical to operations, compliance, or legal matters. The following are key scenarios when back translation should be used:
- Clinical Trials: Back translation is essential to verify the accuracy of trial documents, including consent forms, patient questionnaires, and study protocols. This ensures that the information provided to participants is consistent and legally valid across languages.
- Medical Device Documentation: Whether translating user manuals, instruction booklets, or safety guidelines, back translation ensures that medical professionals and patients can rely on accurate instructions, reducing the risk of errors or misapplication.
- Legal Documents: Back translation helps confirm that legal documents—such as contracts, patents, and certificates—retain their meaning when translated, safeguarding the integrity of legal agreements and preventing costly misunderstandings.
- Financial Statements: Accurate translation of financial documents, such as balance sheets, annual reports, and disclosure agreements, is vital for multinational companies. Back translation helps ensure these documents are legally compliant and that financial data is correctly understood.
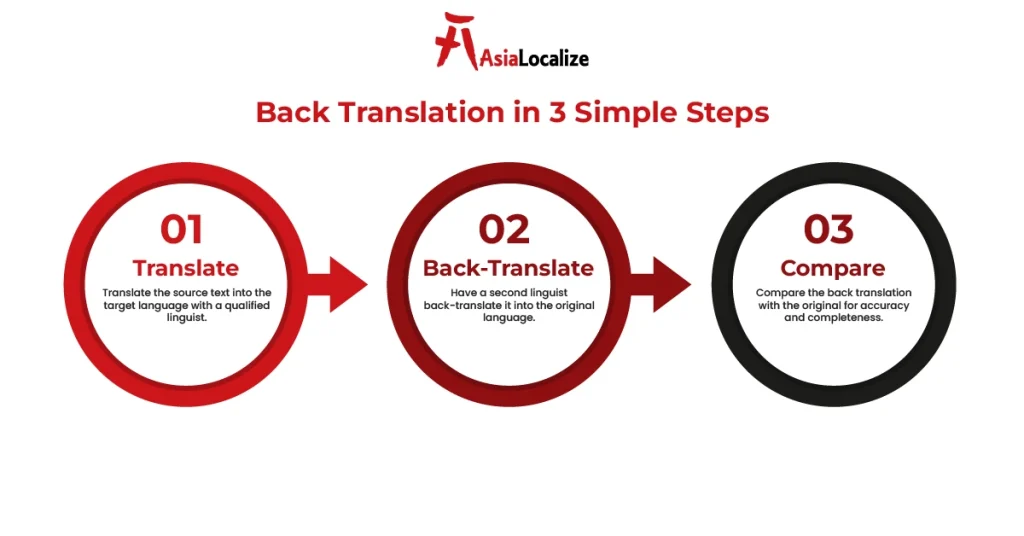
The Back Translation Process: Step-by-Step Quality Assurance
Back translation is a multi-step process designed to verify the accuracy and consistency of the translation. Here’s how it works:
- Original Translation: First, the content is translated from the source language to the target language. This initial translation is the foundation for the subsequent back translation process.
- Independent Back Translation: A different translator or linguist translates the target language content back into the original language. This independent translation is crucial to avoid bias and ensure accuracy.
- Comparison and Analysis: The original and back-translated documents are carefully compared to identify any discrepancies, misinterpretations, or omissions. This is where the attention to detail comes into play.
- Revisions if Needed: If any differences are identified between the two versions, revisions are made to the translation to ensure it aligns with the original meaning. This step is essential to maintain linguistic quality and accuracy.
Industries That Require Back Translation for Quality Assurance
Various industries rely on back translation to ensure their documents are legally compliant, medically precise, and culturally appropriate. Key industries include:
- Life Sciences and Pharmaceuticals: For FDA submissions, clinical trials, and patient-facing documents, back translation is essential to ensure safety and compliance across languages.
- Legal: Back translation is used in the legal industry to verify the accuracy of contracts, licenses, patents, and other important documents.
- Finance: Ensuring that annual reports, financial statements, and contracts are accurately translated and comply with international regulations.
- Marketing and Branding: Back translation can also play a role in marketing, ensuring that brand messaging and advertising materials retain their meaning in different markets, maintaining consistency and cultural relevance.
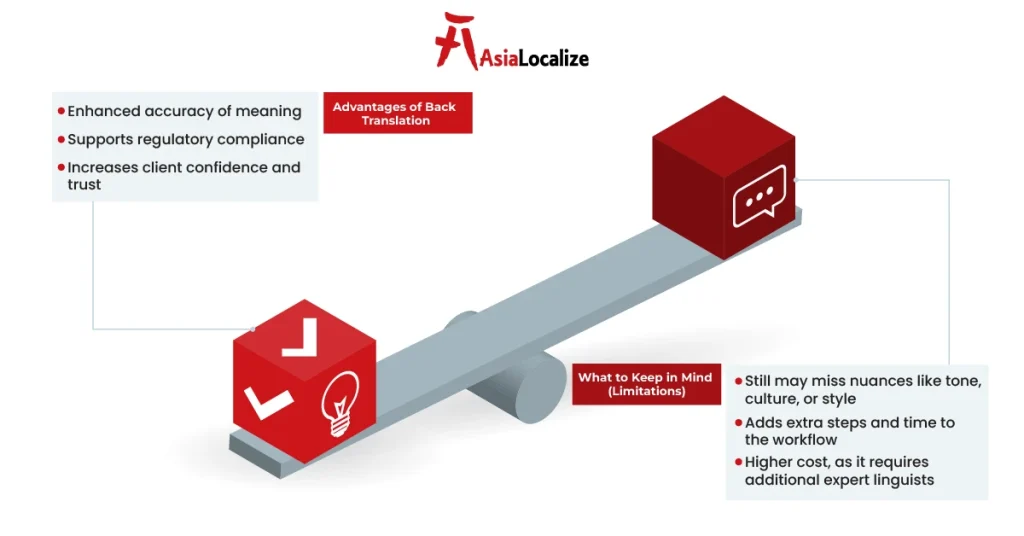
Advantages and Limitations of Back Translation
Like any quality assurance method, back translation offers clear benefits—but it’s not without its drawbacks. Understanding both sides helps you decide when it’s worth the investment.
Advantages:
- Enhanced Accuracy:
When you translate a document back into its original language, you can easily verify that the core meaning and the intent of the message are preserved. And as mentioned above, this is especially important for high-stakes content like protocols or legal contracts.
- Regulatory Compliance:
In highly regulated fields like pharmaceuticals, medical devices, and legal services, back translation is often required or strongly recommended by agencies (e.g., FDA, EMA). It helps demonstrate due diligence and adherence to international standards.
- Increased Client Confidence:
Clients gain peace of mind knowing that critical messaging has been rigorously validated and doubly checked and revised. This trust is crucial when it comes to reputation, safety, or legal risks.
Limitations:
- Time-Consuming:
Adding a second translation step naturally extends timelines—something to consider in fast-paced projects or urgent rollouts.
- Costly:
Specialized back translation—especially in technical or regulated domains—involves expert linguists, which increases project expenses and is usually treated as a separate service.
- Not Always Comprehensive:
While back translation can catch many errors, it may not detect all issues, especially those tied to cultural nuance, idiomatic expression, or tone. It validates linguistic fidelity, not contextual or emotional resonance.
To get the best of both worlds, deploy back translation selectively for high-risk content, then layer it with subject matter experts’ review and in-market QA to cover cultural nuance.
Verify Accuracy with Professional Back Translation Services
Back translation is a powerful tool to ensure the accuracy and reliability of critical documents across industries. If your project involves legal contracts, pharmaceutical studies, or financial documents, back translation can provide the extra layer of assurance needed to maintain compliance and clarity.
Request our back translation services when precision is critical to your business success and compliance across different languages and markets. But always make sure to include the extra step in your budget and timeline, and keep track of any important changes during the reconciliation process. This will help change back translation from just a routine task into a true way to improve quality.