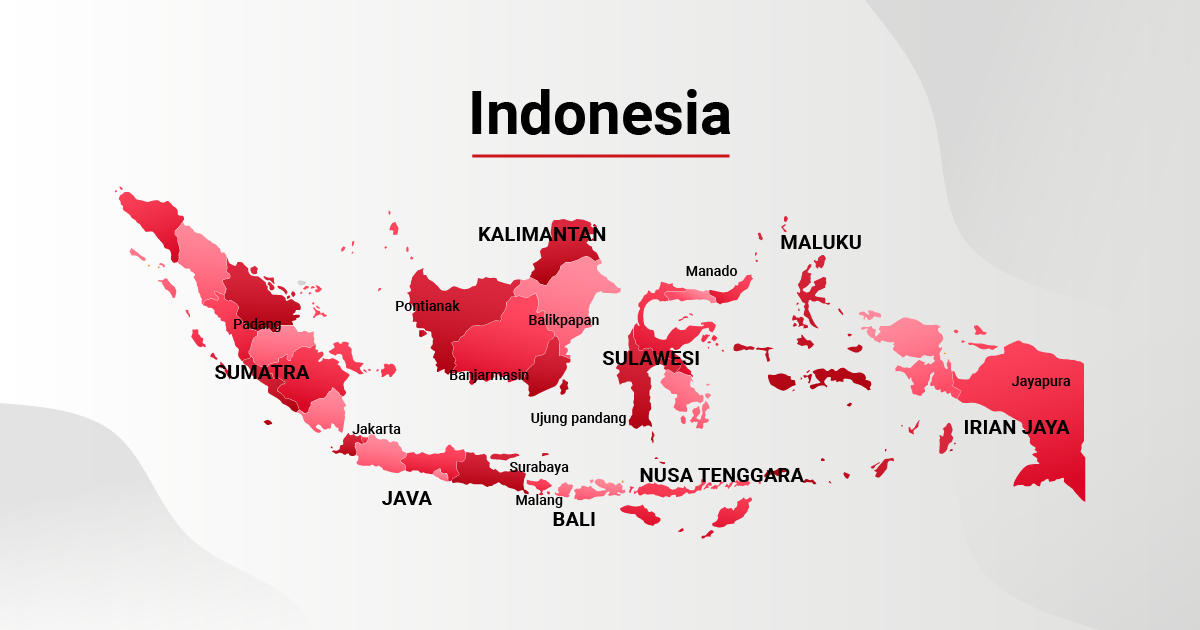
With over 800 languages, Indonesia is renowned for its linguistic and cultural diversity—no wonder it’s the second-largest country with the most linguistic diversity after Papua New Guinea.
However, with such diversity comes many challenges for businesses looking for ways to cultivate the untapped potential of such a lucrative market.
Planning to enter Indonesia requires more than just a decision; it necessitates full awareness of the linguistic and cultural hurdles you will stumble into!
In this post, we’ll equip you with the knowledge you need about the languages spoken in Indonesia to make a 180-degree turn in your business journey toward the Indonesian market.
Bahasa Indonesia: The National Language
Over 97% of Indonesians are fluent in Bahasa Indonesia, the official language of Indonesia. It stems from Malay, which belongs to the Austronesian language family.
For centuries, Malay has served as the region’s lingua franca and as one of the official languages of several other countries, such as Malaysia, Singapore, and Brunei Darussalam, which formed many varieties of Malay.
Besides Malay, Bahasa Indonesian is influenced by other local languages like Javanese, Minangkabau, and Sundanese and some foreign languages such as English, Arabic, Dutch, Sanskrit, and Portuguese.
Bahasa Indonesian language is used in education, business, government, and the Indonesian media.
The influence of Bahasa Indonesia extends far beyond the borders of Indonesia. Surprisingly, it is spoken in the Philippines, the US, Singapore, the Netherlands, Saudi Arabia, and several other countries.
Regional Languages of Indonesia
With over 718 regional languages spoken across Indonesia, languages are spoken in specific areas across the country by varying numbers of speakers up to thousands.
Indonesia is home to 43 regional lingua francas, which serve as the primary means of communication in their respective regions. These can be broadly categorized into Malayic and non-Malayic languages, each with its own unique characteristics and usage.
Major Regional Languages:
The Javanese language
Actually, 30-45% of Indonesians speak the Javanese language, also known as Jawa. It’s the most widely spoken native language in the region.
Javanese is primarily spoken on the island of Java, which is the most populous island in Indonesia. It’s predominantly used in the central and eastern parts of Java, particularly in provinces such as Central Java, East Java, and West Java.
Javanese is also spoken locally in some Malaysian and Singaporean regions.
Sundanese
Sundanese is a Malayo-Polynesian language that is widely spoken in Western Java, Lampung, Banten, and Jakarta.
15% of the Indonesian population speak Sundanese, which reaches over 32 million native speakers.
It has its own writing system derived from old Sundanese and influenced by the Pallava script from South India.
Madurese
10 to 13 million people speak the Madurese language on Madura Island, in eastern Java, and the Kangean and Sapudi islands, which equate to 5% of the population.
Minangkabau
The Minangkabau language, a variant of Malay, is spoken by over 5 million Indonesians in West Sumatra, western Riau, South Aceh Regency, Bengkulu, and Jambi.
It serves as a lingua franca along the coast of North Sumatra.
Buginese
Buginese, known also as Bugis, is spoken widely in southern Sulawesi.
There are 4 million Buginese native speakers in the region.
The Influence of Foreign Languages
Historical influences, including the era of the Dutch East India Company, have shaped Indonesia’s linguistic landscape.
This period of colonization, which lasted for a significant portion of the 17th to the 20th centuries, introduced Dutch as a prominent language in education, governance, and commerce.
While Dutch is no longer widely spoken among the general population, its legacy can still be found in certain legal and administrative contexts.
English
Actually, 30.8% of the population speaks English. Many linguists already consider it a lingua franca, and others view it as a foreign language.
English has become a critical language for trade and investment in Indonesia. In addition, the Indonesian Ministry of Education and Culture has recognized the importance of English in business and has incorporated it into the national education curriculum.
Many universities and business schools emphasize English proficiency, offering programs taught entirely in English to prepare students for the global job market.
Other Foreign Languages
In Indonesia, foreign languages such as Mandarin, Arabic, Japanese, Korean, French, and German are taught in schools and higher education institutions to varying extents.
Read More About: Languages Spoken in Taiwan
AsiaLocalize is Your Trusted Language Service Provider for Accurate Indonesian Translations
Wondering how to take your next steps on your way to Indonesia? We’re here to provide you with 100% reliable Indonesian translation services, conveying your business message faithfully and accurately.
Our team is comprised of native Indonesian experts who will build a localization strategy and action plan to start on the right foot in the Indonesian market.
We also have the most advanced technology tools to empower our translators to speed up the process while maintaining the highest quality standards.