Over 900 billion people speak Mandarin worldwide. The influence of the language extends far beyond China, making it an indispensable tool for engaging with Chinese-speaking communities across the globe.
The growing influence of Chinese-speaking markets offers vast opportunities for businesses to grow and thrive. However, success in these regions requires more than ambition; it calls for a thoughtful strategy that aligns with the cultural and linguistic preferences of these communities.
In this guide, we’ll explore the key countries where Mandarin Chinese is prevalent, equipping you with the insights you need to build strong partnerships and achieve sustainable success.
What Are the Main Chinese Speaking Countries?

Mandarin Chinese in Mainland China and Taiwan

Mainland China is often regarded as the birthplace of Mandarin, with the language (普通话 – Pǔtōnghuà) serving as one of the national languages. It’s primarily based on the Beijing dialect, which is why it carries unique phonetic and tonal characteristics that distinguish it from other Chinese dialects.
Over 80% of the population in Mainland China speaks Mandarin, making it a vital aspect of daily communication, education, and media.
Taiwan is another prominent area where Mandarin is widely spoken and is the official language.
However, Mandarin in Taiwan, often referred to as ‘Taiwanese Mandarin,’ is distinct in its use and incorporates elements from local dialects, particularly Hokkien, a Southern Min dialect widely spoken in Taiwan.
This blend creates a unique linguistic environment where Mandarin retains its standard form while also reflecting local nuances, such as unique expressions or idioms, accents, and vocabulary.
Hong Kong and Macau: Where Cantonese Meets Mandarin
Cantonese is spoken in Hong Kong and Macau, serving as the primary medium of communication among the local population.
However, there has been a noticeable shift in recent years with the increasing influence of Mandarin, particularly in educational institutions and business environments.
As Hong Kong and Macau integrate more closely with Mainland China, Mandarin’s presence has grown significantly. Schools are incorporating Mandarin into their curriculums, making it essential for students to learn the language alongside Cantonese.
In the business sector, Mandarin is not just important but increasingly so for effective communication and collaboration with partners and clients from Mainland China.
Chinese Speaking Countries in the Southeast Asian Region
Mandarin Chinese in Singapore and Malaysia
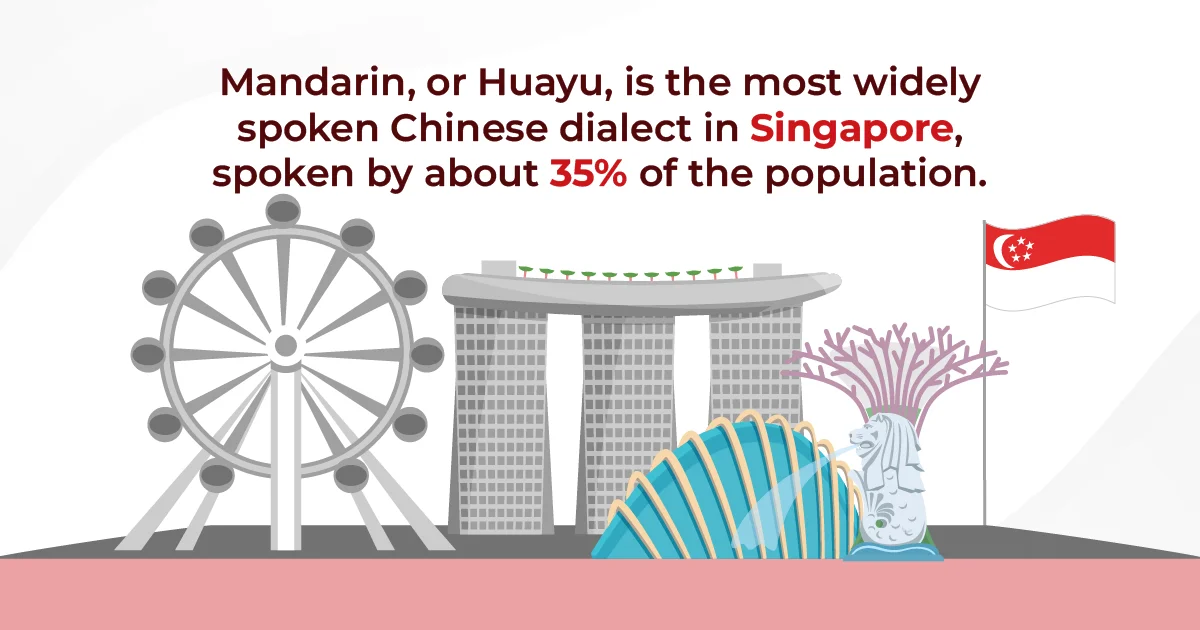
Mandarin Chinese is one of the official languages in Singapore, alongside English, Malay, and Tamil. The promotion of Mandarin Chinese language is a significant aspect of Singapore’s bilingual education system, which strives to uphold both English and a mother tongue language. As a result, Mandarin is taught in schools, enabling students to achieve proficiency in the language from an early age.
35% of Singapore’s population speaks Mandarin, making it a vital component of everyday communication and cultural expression in the nation.
In Malaysia, Mandarin is also widely spoken, particularly among the ethnic Chinese population. The presence of Mandarin can be attributed to a long history of Chinese migration to the region.
Within Malaysia, Mandarin coexists with various regional Chinese dialects, such as Hokkien and Cantonese.
Thailand, Indonesia, and Beyond

Thailand is home to over 8 million Chinese speakers, many of whom are ethnically Chinese.
Mandarin is commonly spoken within Chinese communities, and many families actively maintain their linguistic heritage through language schools and community programs.
In Indonesia, a substantial Chinese community has existed for centuries, resulting from various waves of migration. Here, Mandarin is spoken alongside a variety of regional Chinese dialects, such as Hokkien and Cantonese.
The Chinese-Indonesian population, despite facing historical challenges, has significantly influenced Indonesia’s economy, cuisine, and cultural practices.
Vietnam also hosts a notable Chinese community, particularly in urban areas like Ho Chi Minh City and Hanoi. Mandarin and regional dialects thrive within these communities, often used in familial and cultural contexts.
Mandarin Chinese in the United States

The Chinese-speaking population in the United States has been steadily growing, with over 3 million Chinese speakers across the country. Significant concentrations can be found in major metropolitan areas such as New York and California.
In addition to the United States, there are other countries with significant Chinese-speaking communities. Canada, for instance, is home to approximately 450,000 Chinese speakers. The largest populations are found in cities like Vancouver and Toronto.
Australia also boasts a notable Chinese-speaking population, exceeding 700,000 speakers.
Are you looking for professional Chinese translation services? With AsiaLocalize, we offer solutions powered by our native Chinese speakers in almost all dialects.
We customize our solutions based on your needs and your target market, working according to your timeline and within your budget.